
Sinus Surgery
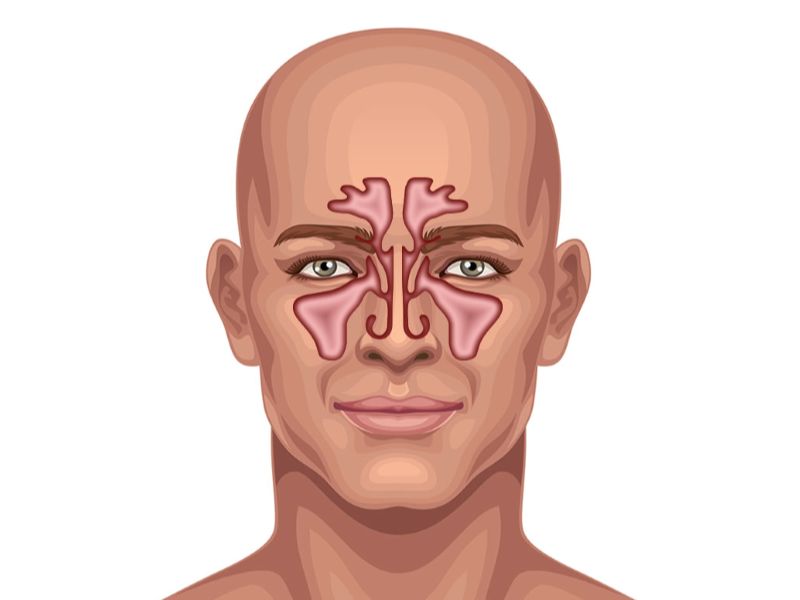 Sinusitis
Sinusitis
Sinusitis is an inflammation of the paranasal sinuses, typically the result of bacterial or viral infection.
Sinus Surgery
Endoscopic sinus surgery involves the use of endoscopes, (fine fibreoptic telescopes) and instruments to open the natural drainage pathways of the sinuses. Abnormal tissue is removed to allow adequate drainage. Once this is achieved the infected mucosa (lining) can return to normal.
The surgery is usually performed through the nostrils leaving no external scars. It is common to have a blocked nose for 1–2 weeks post–operatively but it is rare to have significant pain or swelling.

